Ethiopia Investment and Trade Opportunities: Presented to Malaysian Investors
space
Ethiopian embassy in Jakarta accredited to Malaysia
March 2021
space
SPACE
Article by:
space
Mr Alemayehu Desta
Second Secretary
Embassy of the FDR Ethiopia in Jakarta, Indonesia
(Accredited to Singapore, and Malaysia)
SPACE
1. Ethiopia at a Glance
Official Name: Federal Democratic Republic of Ethiopia (FDRE)
Political system: Federal State with multi-party system
Capital City: Addis Ababa, seat of the African Union (AU) and United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (ECA)
Area: 1.104 million square kilometers
Population: Appx. 112 million
Language: Multiethnic state with more than 80 languages. Amharic is the working language of the federal government. English is taught in schools and is the main business language.
Location: Strategically located as a jumping off point in the Horn of Africa, close to the Middle East and Europe markets.
Arable land: 513,000 Km2 (45%)
Irrigated land: 34,200 Km2 (3%)
Population density: Appx. 90.5 per Km2
Climate: Temperate in the highlands, ranging from 20°C to 30°C (68°F to 86°F) and hot in the lowlands, often reaching 45°C (113°F). Rainfall ranges from 200 mm to 2000 mm.
GDP per capita: US$ 900 (2019)
Rainy Seasons: Abundant rain in June through August; mild rains in February and March.
Topography: Ethiopia has an elevated central plateau varying in height from 2,000 to 3,000 meters above sea level. In the North and center of the country there are some 25 mountains whose peaks reach over 4,000 meters. The most famous Ethiopian river is the Blue Nile or Abay, which flows a distance of 1,450 kilometers from its source to join the White Nile at Khartoum.
Economy: More than 70% of the population earns a living from agriculture. Agriculture is the backbone of the national economy, and the principal exports from this sector are coffee, oilseeds, pulses, flowers, vegetables, sugar, and foodstuffs for animals. There is also the thriving livestock sector, exporting cattle, hides, and skins.
space
space
2. Ethiopia-Malaysia Relations
The Diplomatic relations between Ethiopia and Malaysia was established in 1965. Both countries have been keen to reinforce their overall relations. In this connection, higher officials and delegations have started making various visits starting from the 1990s.
The commencement of direct flight by Ethiopian Airlines to Kuala Lumpur is playing a major role in promoting trade and investment between the two countries.
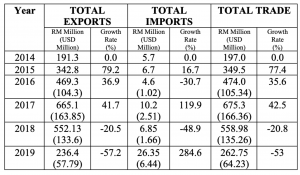
Trade between the two countries is showing a progressive trend in recent years. In 2017 Ethiopia has imported products worth 340,705,770.51 USD and exported items worth 723,616.49 USD. Ethiopia exports leather and leather products, raw meat and vegetable products to Malaysia and imports sugar, cotton, fatty acid, vegetable oil, paper, and paper products, Medical equipment, soap, and Detergent. It imports 95% its demand from edible oil producing countries like Malaysia, Indonesia, and Singapore. The cooking oil demand of the Ethiopian market is 507,191 tonnes annually, of which almost 95% is imported edible oil. Both countries signed Bilateral Investment Treaty (BIT) in 1998.
space
Source: Ministry of International Trade and Industry (MITI), Malaysia
space
space
3. Economic Indicators
– Ethiopia’s economy experienced strong, broad-based growth averaging 11% a year from 2010/11 to 2019/20, Ethiopia’s real gross domestic product (GDP) growth slowed down to 6.1% in 2019/20 due to COVID-19.
– Ethiopia – the second most populous country in Africa is one of the fastest growing states among the 188 IMF member countries. This growth was driven by government investment in infrastructure, as well as sustained progress in the agricultural and service sectors. The GDP in 2019 reached $92.154 billion where the services have surpassed agriculture as the principal source of GDP.
– Fast economic growth, conducive investment climate, large market size, and high-level government commitment towards FDI attraction have contributed to the growth of FDI inflow into Ethiopia-making the country the largest recipient of FDI in East Africa and the 4th largest on the continent.
– East Africa, the fastest-growing region in Africa, received $8.9 billion in FDI in 2018, of which Ethiopia absorbed more than a third and is now the 4th largest recipient of FDI in the continent of Africa and the largest in East Africa. (UNCTAD, World Investment Report 2019 and FDI Intelligence).
– 46% growth in FDI inflow-one of the most dynamic and largest FDI recipients in Africa (UNCTAD World Investment Report, 2017)
– Ethiopia is ranked 57th, better than its regional peers for its conducive macroeconomic environment.
– Recognized by UNCTAD for promoting investment in the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs)
– Recognized by the World Bank through its “Star Reformer Award” for Ethiopia’s outstanding performance on investment policy reform and promotion
– Ethiopia exports oil seeds like Soyabeans, Sesame, Niger seed, Sunflower seed, Almond seed and pulses like Green mung bean, Red kidney beans, Chick pea, Lentil, red, brown, Field pea, Faba beans, Vetch seed, Lupin seed, Black cumin, and flower like Gypsophila, Veronica, Rose, Hypericum, Chrysanthemums. Coffee and gold are also the top export products.
Economic Growth 2012/13-2016/17
Export of Goods
Source: National Bank of Ethiopia
– Asia, Europe and Africa are the major destinations for Ethiopian merchandise export. Asia accounted for 36.4% of Ethiopia’s total exports. Saudi Arabia was the largest market for Ethiopia’s export with 19.0 % share in total export earnings from Asia, followed by United Arab Emirates (11.5 %), Japan (10.4 %), Israel (9.4 %), China (7.7 %), South Korea (5.9 %), India (5.2 %), Singapore (3.6 %), Yemen (3.5 percent), Indonesia (2.7 %) and Taiwan (2.1 %). These countries altogether accounted for 81.0 % of Ethiopia’s total export revenue from Asia.
– Europe had 33.6 % share in Ethiopia’s total export revenue, with the Netherlands taking 30.8 % share, followed by Switzerland (19.8 %), Germany (16.0 %), Belgium (8.0 %), Italy (4.4 %), Turkey (3.4 %), United Kingdom (3.3 %) and France (2.8 %). On the while, these countries had 88.6 % share in Ethiopia’s total exports earnings from Europe.
– America accounted for 10.6 % of Ethiopia’s total export revenue, of which 67.4 % was from exports to the United States, 4.6 % to Canada and 0.7 % to Mexico. These three countries had 72.7 % share in Ethiopia’s total exports to America.
Source: National Bank of Ethiopia
Import of Goods
– Total merchandise import bill reached USD 13.9 billion depicting 8.1 % year-on-year decline mainly due to lower import bill of fuel, capital goods and consumer goods. Payments for semi-finished goods, raw materials and miscellaneous goods, however, registered annual increment. Hence, import to GDP ratio declined to 12.9 % compared with 15.8 % a year ago.
– In 2019/20, Asia accounted for 60.6 % of the total imports of Ethiopia. The major imports from Asia originated from China (42.9 %), India (12.9 %), Kuwait (12.9 %), U.A.E (6.5 %), Saudi-Arabia (5.4 %), Indonesia (3.4 %), Malaysia (2.45%), Singapore (2.3 %), South Korea (2.2 %) and Japan (2.1 %) whose combined share stood at 90.8 %.
– Europe accounted for 21.8 % share of Ethiopia’s imports with the major trading partners being Turkey (20.2 %), Ukraine (11.2 %), Germany (9.8 %), United Kingdom (9.8 %), Italy (8.7 %), France (8.5 %), Belgium (8.0 %), the Netherlands (5.1 %), Spain (2.7 %), Switzerland (2.4 %) and Russia (2.3 %). These countries jointly constituted 88.7 % of Ethiopia’s total imports from Europe.
– About 9.3 % of Ethiopia’s imports came from America, of which 82.7 % was from the United States, 5.9 % from Canada and 1.3 % from Brazil.
space
space
4. Why Invest in Ethiopia?
– Political and social stability
– Growing Economy
– Excellent climate and fertile soils
– Strong guarantees and protections
– Young and trainable labor force
– Regional hub with access to wider market
– Improved economic infrastructure
– Competitive incentive packages
– High government commitment
space
space
5. Investment Opportunities for Malaysian Companies
5.1 Agriculture
– Ethiopia’s vast land, favorable climate, and water and land resources combine to make it an incredible hub for investment. Located in the horn of Africa, within easy reach of the Horn’s major ports, Ethiopia is close to its traditional markets for export products – the Middle East and Europe. This geographical proximity provides major exporters in the world unparalleled access to the Ethiopian floricultural market.
– The total land area coverage is about 111.5 million ha, of which 74.3 million ha is suitable for agriculture.
Investment Opportunities
– Sugarcane, horticulture, floriculture, forestry (including rubber tree plantation, fiber crops: (cotton, jute) animal husbandry, etc. Eighteen major agro-ecological zones have been identified in the country, and over 3 million ha land has been made available for investment. Ethiopia offers one of the largest and most diverse agricultural investment opportunities on the continent.
space
5.2 Textile and Apparel
– Ethiopia’s textile and garment industry witnessing rapid growth, as a number of domestic and multinational firms are being engaged in the production of textile and apparel for domestic and global markets. In the path to industrialize Ethiopia, the sector is given prominent position in boosting export, creating job opportunities, and as a model to other sectors as well.
– This recent surge in Ethiopia’s textile and apparel production and export to the global markets shows that the country has the potential to become one of the leading textiles and Apparel hubs of Africa, of exporting the equivalent of 30 billion USD with bold vision of transforming the action into compelling new apparel sourcing hub for brand, retails and their suppliers.
– Due to focused strategy and support of the government, in recent years, Ethiopia has grown spectacularly as a sourcing destination for apparel in recent years attracting most of the FDI in the sector.
Investment Opportunities
– Ginning, integrated textile mills, spinning, weaving and/or knitting, dyeing and printing,
– Production of garments; the manufacturing of knitted and crocheted fabrics, carpets, and sportswear, among others
space
5.3 Leather and Leather Products
– Ethiopia has a cattle population of more than 53 million, and sheep and goat population of 25.5 and 24.1 million, respectively. This makes Ethiopia the 1st from Africa and the 9th from the world in its cattle population which enable the country to have a strong raw material base for the leather industry.
– Only 50% of hides and skins potential are being utilized currently.
– Ethiopia has a potential for price competitive and quality supply of skins and hides: The Ethiopia highland sheepskins have got a worldwide reputation in terms of quality, thickness, flexibility, strength, compact structure, and a clean inner surface.
Investment Opportunities
– Tanning of hides and skins up to finished level;
– Manufacturing of luggage (such as handbags), saddle and harness items, footwear, and garments; and
– Integrated tanning and manufacturing activities.
space
5.4 Pharmaceutical
Pharmaceutical manufacturing is a nascent sector in Ethiopia with an annual 15% growth rate; import-dependent with an opportunity to invest and manufacture.
Key Sectors and incentive
– Tailored fiscal incentives to manufacturers including exemption from income tax up to 14 for Active pharmaceutical ingredient manufactures, 8 – 10 years for enterprises engaged in manufacturing of final drugs/ formulation, and up to 6 years for enterprises engaged in pharmaceutical packaging.
– Exemption from duties and other taxes on imports of machinery, equipment, construction materials, spare parts, raw materials, vehicles, loss carryforward, and full export duty exemption for manufactures
– Similar to other sectors, manufactures of pharmaceutical products are allowed duty-free import of capital goods and construction materials to facilitate in the establishment of a plant that adheres to the national General Manufacturing Practices guidelines, and for local manufacturing.
– Government is working towards setting an import tariff on non -Ethiopian Pharmaceutical Supply Agency imports to unify the advantages provided to local manufacturers in serving the domestic market; at the same time, applying the tariff only to non-EPSA imports ensures that EPSA can continue benefiting from the lower prices offered by domestic manufacturers.
space
5.6. Agro-Processing
Key reasons to invest
– Ethiopia’s plentiful agricultural resources including cattle, forests, cropland, suitable climate condition, and labor force are critical inputs for agro-processing industries.
– Ethiopia produces the best Arabica coffee in the world and is known for having a wider genetic variety of coffee than any other coffee producing country.
– Ethiopian coffee is well known for its special aroma and flavor, a uniqueness that makes it preferable for blending with coffee from other countries. Currently, Ethiopia is among the top five coffee exporters in the world.
– Ethiopia produces a variety of different sesame seeds which are highly valued on the international market. Production of sesame in the country has doubled in the past five years.
– Ethiopia ranks first in Africa and tenth in the world by cattle population of 55 million which is a big opportunity for meat processing industry.
– Ethiopia already has well-established partners in the meat trade.
– The size of the livestock population, the natural endowment of favorable climatic condition for improved, high-yielding animal breeds, provides Ethiopia with significant potential to further develop its dairy sector.
– Demand for chicken products is growing quickly in Ethiopia. The Government recently set new targets to bring meat production to 164 tones and egg production to 3.9 billion eggs by 2020 through improved poultry breeds.
– Ethiopia is the tenth largest honey producing country in the world and the largest in Africa. It ranks fourth in the world in terms of bee wax production and export.
– Yields of tomato can reach up to 80 tons per hectare which assures consistent and abundant supply for tomato processing plant.
Investment Opportunities
– Processing of meat and meat product
– Processing of fish and fish product
– Processing of fruit and and/Vegetables
– Manufacturing of edible oil
– Processing of milk and/manufacturing of dairy product
– Manufacturing of starch and starch product
– Processing op pulses, oil seeds or cereals
– Manufacturing of macaroni, pasta and similar products
– Manufacturing of chocolate, candy and biscuits
– Manufacturing of baby foods, roasted and ground coffee and similar products
– Processing of animal feeds
– Processing of alcohol and soft drink
space
5.7 Tourism and Hospitality
– Ethiopia is one of the oldest civilizations, the source of the mighty Nile River, and is endowed with a long-aged heritage and uninterrupted political independence.
– Located in the horn of Africa’s Rift Valley region and known globally as the origin of mankind, Ethiopia offers a variety of tourism attractions such as Natural, Cultural, Historical, Mystical, Athletics, and MICE.
– Ethiopia commands a large and untapped potential for the tourism and hospitality business. The increasing number of tourists and the evolving profile of today’s traveler demand a host of new tourism offerings and infrastructure projects.
– Ethiopia commands a large and untapped potential for the tourism and hospitality business. The increasing number of tourists and the evolving profile of today’s traveller demand a host of new tourism offerings and infrastructure projects.
– MICE Facilities
– Star rated tourist hotels and lodges
– Entertainment and Shopping Centres
– Tourist Information Shops
– Tourist Transport and Travel Services
– Tourism Medical Services
– Food and Beverage Services
– Leisure & Sports
– Education and Training Facilities
– In addition, Addis Ababa’s significance as the political capital of Africa brings a high representation of international and regional organizations, including the seat of the African Union and the United Nations Economic Commission on Africa.
space
5.8. Power
Ethiopia has the second- largest population in Africa (>105 million, ~8.5 % of Africa population), with an expected growth rate of 2.3% per year. Such increase in population size will result in an increase in the number of individuals requiring access to electricity. The government of Ethiopia has set clear power generation and connection targets and sees the private sector as pivotal in meeting intended targets.
Key reasons for investing
– Rapidly growing electricity demand at 30-35% annually mainly as a result of;
– More than 80 GW of exploitable renewable energy reserves;
– Low electricity access provides opportunity for off-grid solutions to thrive because;
– Trainable workforce with competitive wages
– National policy sees Ethiopia as a power supply hub for the East African region through the East African Power Pool
– Investment in on-grid power generation is open to the private sector, mainly targeting foreign direct investment
– Off-grid and mini-grid systems are also a major component of the nation’s plan to increase access to electricity; and engaging the private sector has been championed
– With a dedicated regulator (the Ethiopian Energy Authority) in place, the Ethiopian power sector is semi-unbundled
– The Ethiopian Electric Power (EEP) owns all pubic power generation plants and is a monopoly power transmission provider; EEP also conducts all power purchase contracts with Independent Power Producers
space
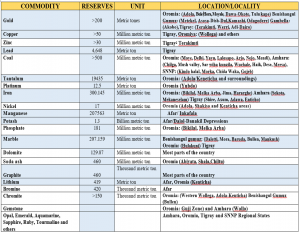
5.9 Mining
Ethiopia’s mining sector has undertaken a major reform programme in recent years. The reform is designed to make it easier than ever to invest in Ethiopia, encourage exploration and mining, and unlock the sectors full potential and value. The reform includes geodata management, transparency and ease of licensing process and the artisanal mining sector among others.
Ethiopia has known occurrences of more than 30 minerals. These include:
– Metallic minerals (gold, platinum, iron, nickel,chromite and base metals);
– Energy minerals (lithium, graphite, tantalum and coal);
– Cement raw minerals (limestone, gypsum, clay, pumice);
– Fertilizer raw minerals (potash and phosphate);
– Ceramics raw minerals (kaolin, feldspar);
– Glass raw minerals (silica sand);
– Dimension stones (marble, granite, limestone, sandstone, diatomite, bentonite, soda ash, salt, graphite and Sulphur);
– Gemstones (opals, emeralds, sapphires)
space
5.10 Information and Communication Technologies (ICT)
– Identified as strategic priorities by the Government of Ethiopia as it will drive and facilitate the transformation of Ethiopia’s predominantly subsistence-agriculture economy to into an information and knowledge-based economy and society, that is effectively integrated into the global economy. Tailored industrial park has been dedicated to the sector.
– Ethiopia’s internet penetration in 2016 was 15.4% while recent statistics show mobile penetration at 63%, with low penetration rates stemming from underdeveloped telecommunications infrastructure. With a population over 100 million and a median age of under 18 years, Ethiopia offers significant opportunities for ICT development.
– In June 2018 Ethiopia’s government announced that it would allow private domestic and foreign investment in a number of sectors including telecoms tentatively opens up one of the last biggest telecoms opportunities in Africa. The government took steps to liberalization this year by issuing an internet service provider license to a local private company.
space
6. Industrial Parks (IP)
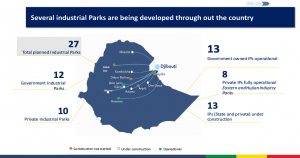
– The Government of Ethiopia, with the vision of making Ethiopia a leading manufacturing hub in Africa, placed a high focus on industrial parks development and expansion.
The government has so far constructed and operationalized over 20 state-of-the-art industrial parks which are located along key development corridors – each with a distinct specialty in a priority sector (Textile & Apparel, Leather & Leather Products, Pharmaceutical, Agro-Processing, and Mixed). Industrial parks allow the investors to get all the necessary services easily at a single place.
– Industrial parks are both government and private owned.Facilities in industrial parks include One-Stop Service, dedicated power sub-station, waste treatment facilities, commercial buildings and housing facilities, health stations, fire brigade, and 24/7 security service.
– With the vision to make Ethiopia a leading manufacturing hub in Africa by 2025, the Government of Ethiopia had placed a high focus on industrial park development and expansion. The GoE has so far constructed and operationalized over 20 state-of-the-art industrial parks which are located along key development corridors – each with a distinct specialty in priority sectors.
space
You can download the detailed version of the investment and trade profile of Ethiopia here:
ETHIOPIA INVESTMENT OPPORTUNITIES TO MALAYSIAN COMPANIES
space
space
Contacts
FDR Embassy in Jakarta
Address: Jl. Aditiyawarman No.21, RT.3/RW.2, Selong, Kec. Kby. Baru, Kota Jakarta Selatan, Daerah Khusus Ibukota Jakarta 12110
Phone: +62 21 22776658
Email: ethembjakarta@gmail.com
Website: www.jakarta.mfa.gov.et
space
space
Additional important contact Address
| Ethiopian Investment Commission
P.O. Box 2313 Tel: +251-11-551 0033 Fax: +251-11-551 4396 E-mail: ethioinvest@investethiopia.gov.et Website: http://www.investethiopia.gov.et/ |
Ministry of Trade
P.O. Box 704 Tel: +251-11-551 8025 Fax: + 251-11-551 5411 Website: http://www.mot.gov.et/home
|
|
| Industrial Parks Development
Corporation (IPDC) Tel: +251-11-661 6986 / 661 6674 E-mail: info@ipdc.gov.et Website: http://www.ipdc.gov.et/index.php/en/
|
Ministry of Foreign Affairs
P.O. Box 393 Tel: +251-11-551 7345 Fax: +251-11-551 4300/ 551 1244 E-mail: mfa.addis@telecom.net.et Website: http://www.mfa.gov.et/
|
|
| Ministry of Industry
P.O. Box 6945 Tel: +251-11-550 7542 Fax: + 251-11-575 9871 Website: www.moin.gov.et
|
Ministry of Labour and Social Affairs
P.O. Box 2056 Tel: +251-11-551 7080 Fax: +251-11-551 8396 E-mail: molsa.comt@ethionet.et Website: http://www.molsa.gov.et/
|
|
| Ethiopian Revenue and Customs Authority
Tel: +251-11-667 3970 Fax:+ 251-11-662 9842 Website: http://www.erca.gov.et/
|
Ethiopian Chamber of Commerce
and Sectoral Associations P.O. Box 517 Tel: 251-11-551 8240 Fax: 251-11-551 7699 E-mail: etchamb@ethionet.et Website: http://www.ethiopianchamber.com/
|
|
| National Bank of Ethiopia
P.O. Box 5550 Tel: +251-11-551 7430 Fax: +251-1-551 4588 E-mail: nbe.excd@ethionet.et Website: http://www.nbe.gov.et/
|
Development Bank of Ethiopia
P.O.Box 1900 Tel: 251-11-51 1188/89 Fax: 251-11-511606 E-mail: dbe@telecom.net.et Website: http://www.dbe.com.et/
|
|
| Addis Ababa Chamber of Commerce
and Sectoral Associations P.O. Box 2458 Tel: 251-11-551 8055 Fax: 251-11-551 1479 E-mail: info@addischamber.com Website: http://addischamber.com/
|